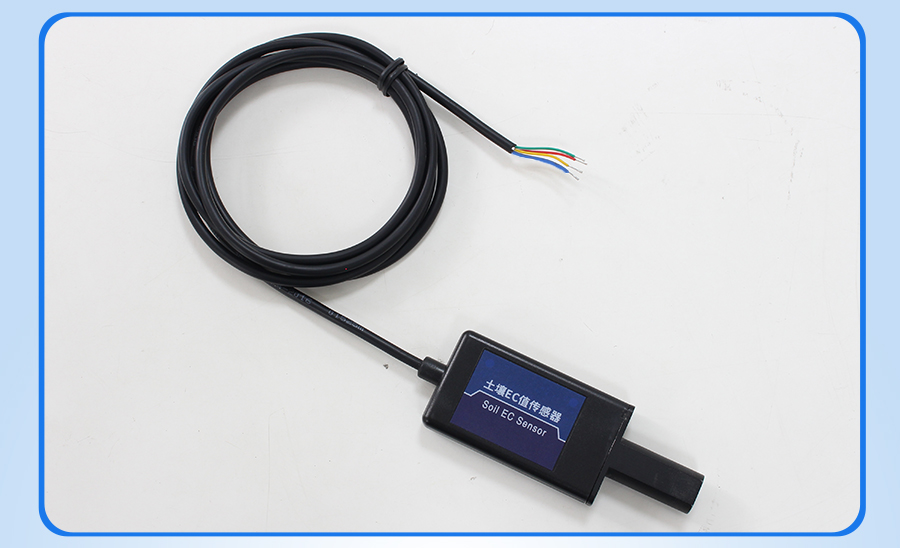
SM3105 using the standard ,easy access to PLC,DCS and other instruments or systems for monitoring 土壤conductivity state quantities.The internal use of high-precision sensing core and related devices to ensure high reliability and excellent long-term stability,can be customized RS232,RS485,CAN,4-20mA,DC0~5V\10V,ZIGBEE,Lora,WIFI,GPRS and other output methods.
Technical Parameters
| Technical parameter | Parameter value |
| Brand | SONBEST |
| Interface | RS485/4-20mA/DC0-5V/DC0-10V |
| Power | DC12~24V 1A |
| Running temperature | -40~80°C |
| Working humidity | 5%RH~90%RH |
Product Selection
Product DesignRS485,4-20mA,DC0-5V,DC0-10VMultiple output methods, the products are divided into the following models depending on the output method.
| Product model | output method |
| SM3105B | RS485总线 |
| SM3105M | 4-20mA |
| SM3105V5 | DC0-5V |
| SM3105V10 | DC0-10V |
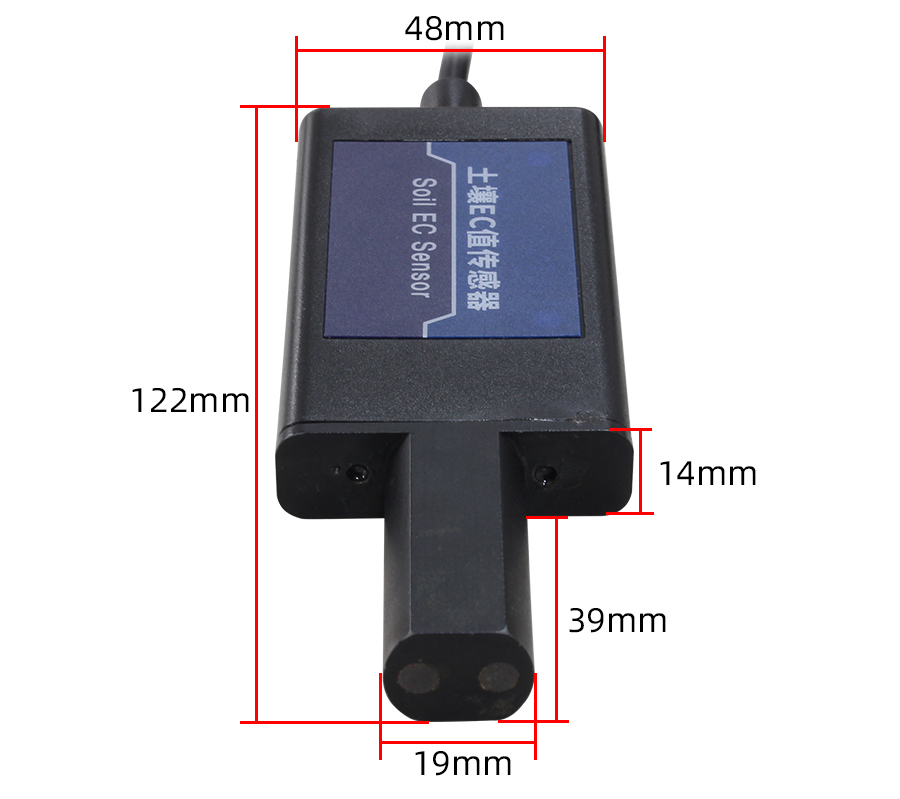
Product Size

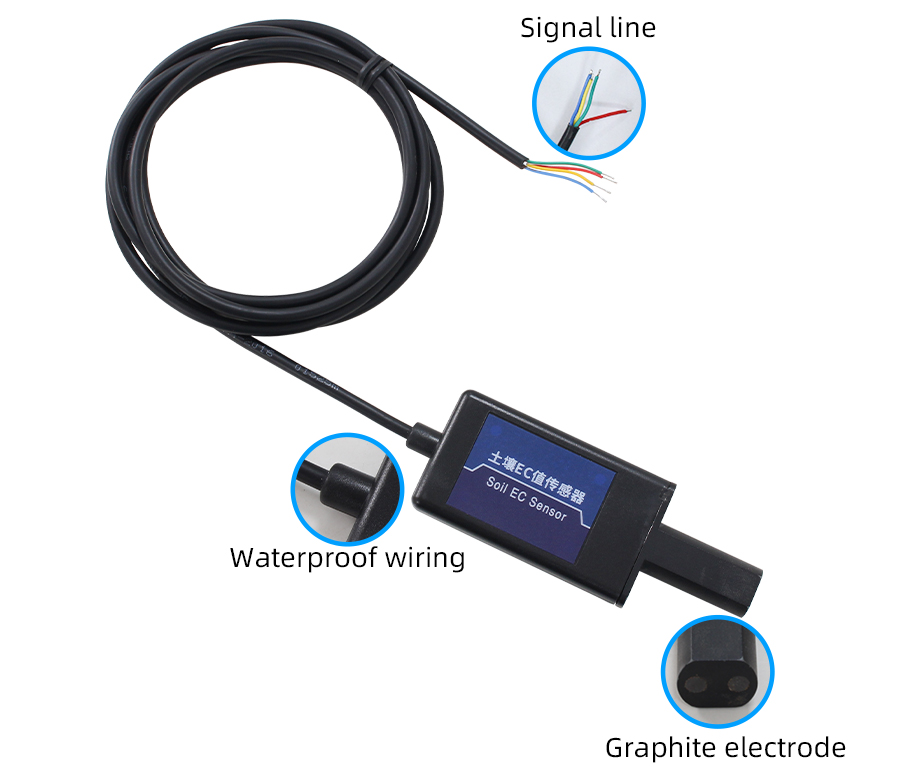
How to wiring?


Why choose this product?



Application solution
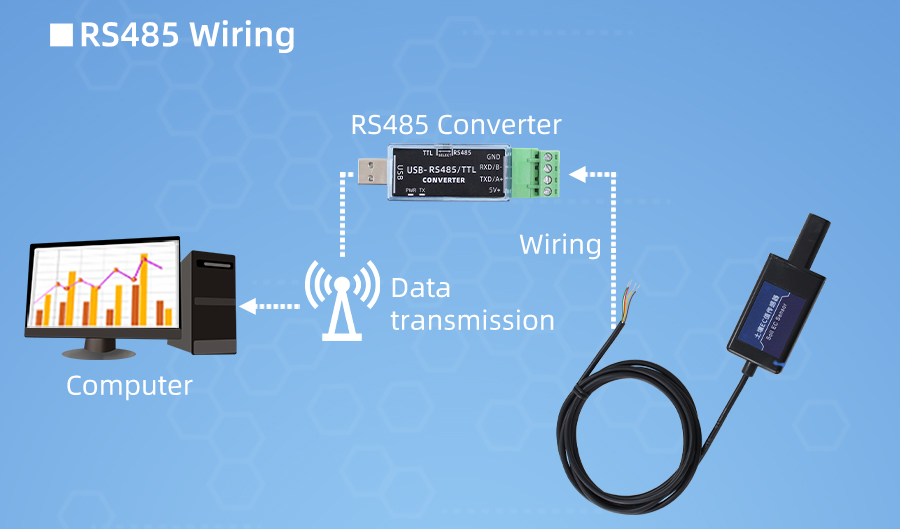
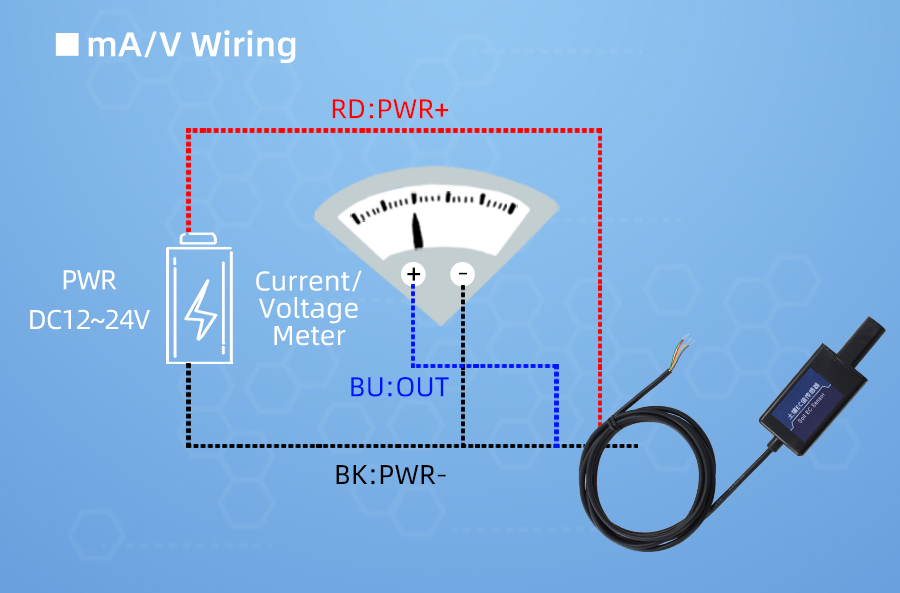
How to use?

| current(mA) | IlluminanceValue (Lux) | Calculation Process |
| 4 | 0.0 | (2000-0)*(4-4)÷(20-4)+0 |
| 5 | 125.0 | (2000-0)*(5-4)÷(20-4)+0 |
| 6 | 250.0 | (2000-0)*(6-4)÷(20-4)+0 |
| 7 | 375.0 | (2000-0)*(7-4)÷(20-4)+0 |
| 8 | 500.0 | (2000-0)*(8-4)÷(20-4)+0 |
| 9 | 625.0 | (2000-0)*(9-4)÷(20-4)+0 |
| 10 | 750.0 | (2000-0)*(10-4)÷(20-4)+0 |
| 11 | 875.0 | (2000-0)*(11-4)÷(20-4)+0 |
| 12 | 1000.0 | (2000-0)*(12-4)÷(20-4)+0 |
| 13 | 1125.0 | (2000-0)*(13-4)÷(20-4)+0 |
| 14 | 1250.0 | (2000-0)*(14-4)÷(20-4)+0 |
| 15 | 1375.0 | (2000-0)*(15-4)÷(20-4)+0 |
| 16 | 1500.0 | (2000-0)*(16-4)÷(20-4)+0 |
| 17 | 1625.0 | (2000-0)*(17-4)÷(20-4)+0 |
| 18 | 1750.0 | (2000-0)*(18-4)÷(20-4)+0 |
| 19 | 1875.0 | (2000-0)*(19-4)÷(20-4)+0 |
| 20 | 2000.0 | (2000-0)*(20-4)÷(20-4)+0 |
For example, the range is 0~2000Lux, the analog output is 0~5V voltage signal, Illuminance and voltage The calculation relationship is as shown in the formula: C = (A2-A1) * (X-B1) / (B2-B1) + A1, where A2 is Illuminance range upper limit, A1 is the lower limit of the range, B2 is voltage output range upper limit, B1 is the lower limit, X is the currently read Illuminance value, and C is the calculated voltage value. The list of commonly used values is as follows:
| voltage(V) | IlluminanceValue (Lux) | Calculation Process |
| 0 | 0.0 | (2000-0)*(0-0)÷(5-0)+0 |
| 1 | 400.0 | (2000-0)*(1-0)÷(5-0)+0 |
| 2 | 800.0 | (2000-0)*(2-0)÷(5-0)+0 |
| 3 | 1200.0 | (2000-0)*(3-0)÷(5-0)+0 |
| 4 | 1600.0 | (2000-0)*(4-0)÷(5-0)+0 |
| 5 | 2000.0 | (2000-0)*(5-0)÷(5-0)+0 |
| 10 | 750.0 | (2000-0)*(10-4)÷(20-4)+0 |
For example, the range is 0~2000Lux, the analog output is 0~10V voltage signal, Illuminance and voltage The calculation relationship is as shown in the formula: C = (A2-A1) * (X-B1) / (B2-B1) + A1, where A2 is Illuminance range upper limit, A1 is the lower limit of the range, B2 is voltage output range upper limit, B1 is the lower limit, X is the currently read Illuminance value, and C is the calculated voltage value. The list of commonly used values is as follows:
| voltage(V) | IlluminanceValue (Lux) | Calculation Process |
| 0 | 0.0 | (2000-0)*(0-0)÷(10-0)+0 |
| 1 | 200.0 | (2000-0)*(1-0)÷(10-0)+0 |
| 2 | 400.0 | (2000-0)*(2-0)÷(10-0)+0 |
| 3 | 600.0 | (2000-0)*(3-0)÷(10-0)+0 |
| 4 | 800.0 | (2000-0)*(4-0)÷(10-0)+0 |
| 5 | 1000.0 | (2000-0)*(5-0)÷(10-0)+0 |
| 6 | 1200.0 | (2000-0)*(6-0)÷(10-0)+0 |
| 7 | 1400.0 | (2000-0)*(7-0)÷(10-0)+0 |
| 8 | 1600.0 | (2000-0)*(8-0)÷(10-0)+0 |
| 9 | 1800.0 | (2000-0)*(9-0)÷(10-0)+0 |
| 10 | 2000.0 | (2000-0)*(10-0)÷(10-0)+0 |
| 15 | 1375.0 | (2000-0)*(15-4)÷(20-4)+0 |
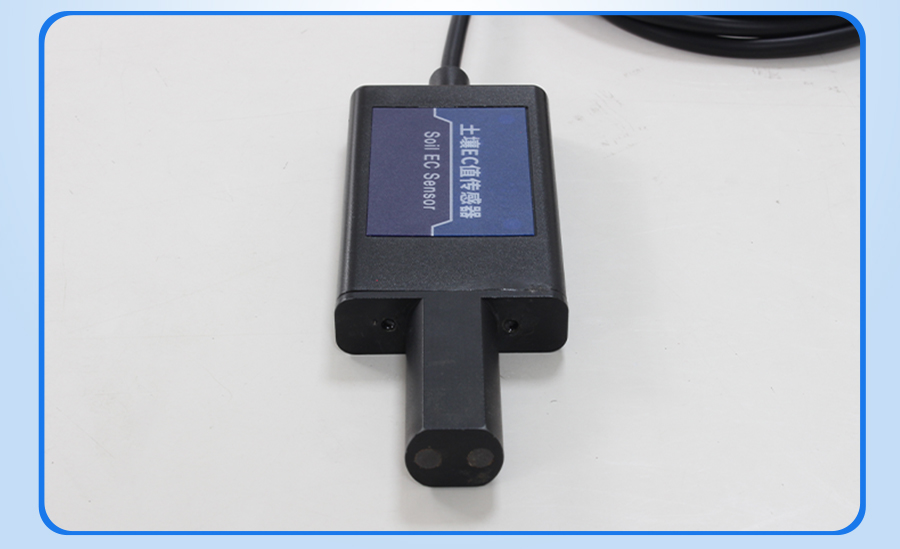
Product Pictures

Product Pictures


